LED point lights have transformed outdoor illumination. They provide economical, long-lasting, and eye-catching answers for building exteriors, promotion, and city decoration. Grasping the science behind this lighting method helps you value its benefits and choose wisely for your projects. This detailed guide examines the physics, tech, and uses of these lights, highlighting their part in current lighting.
What Are LED Point Lights?
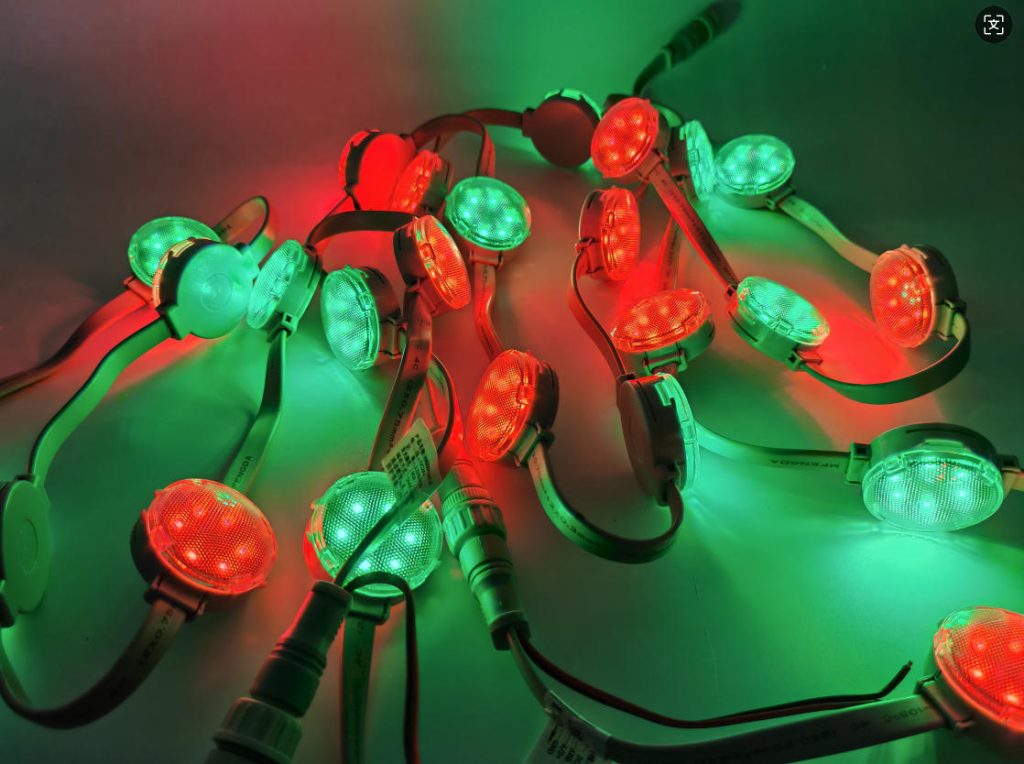
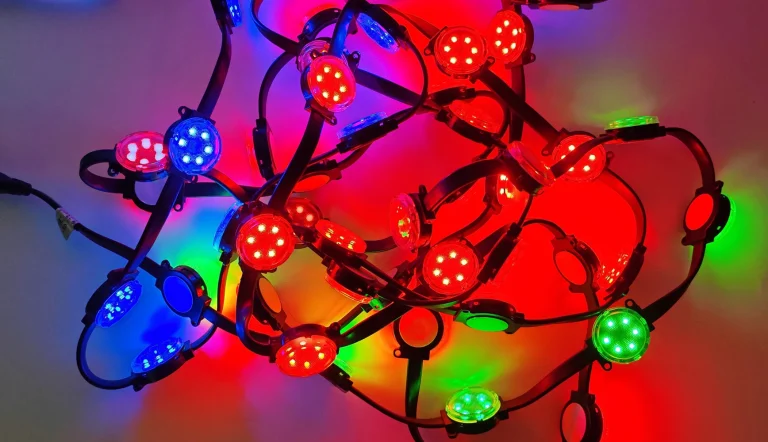
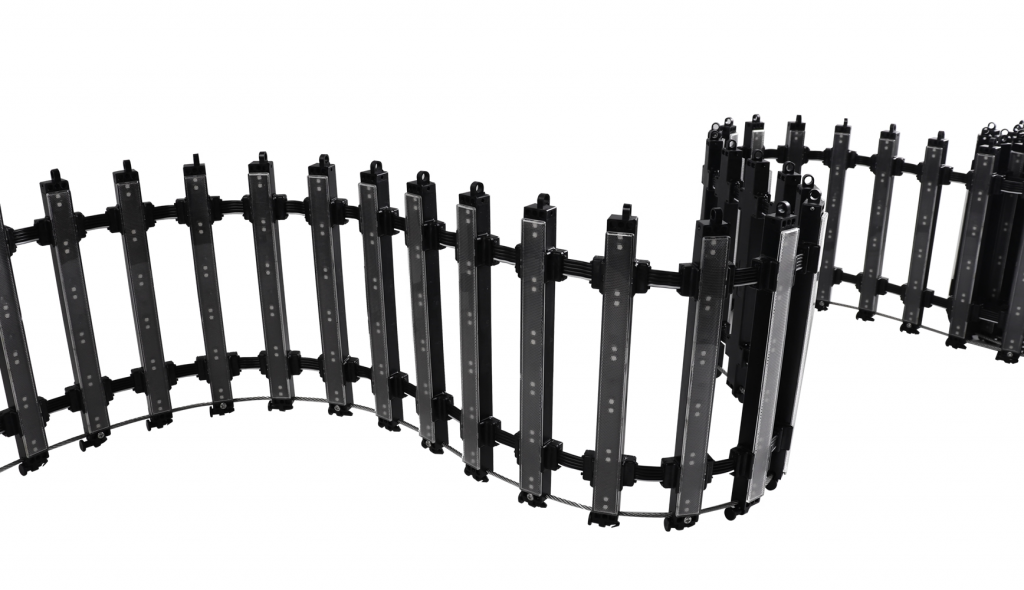
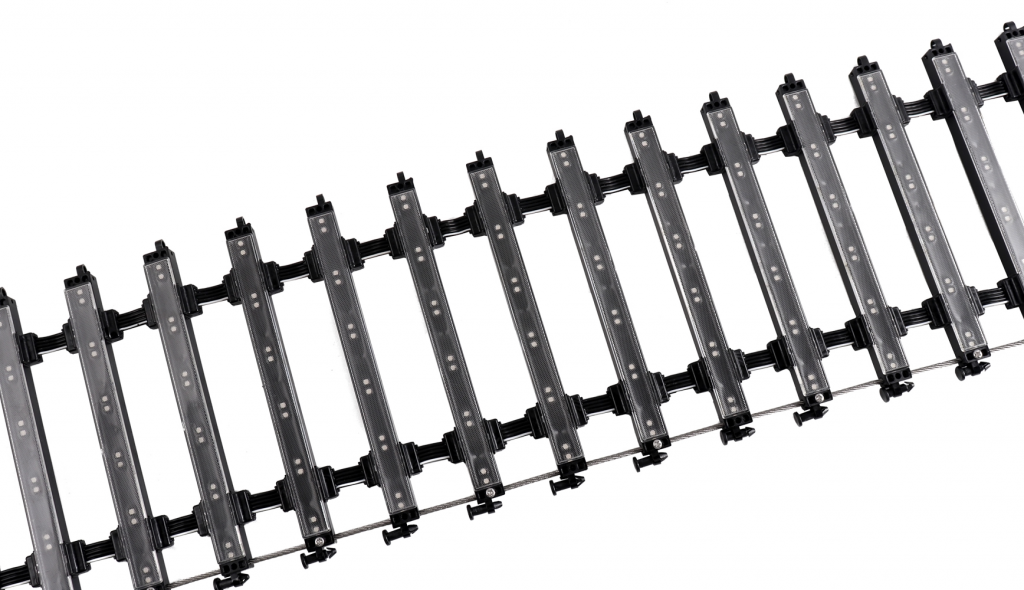
LED point lights are small, potent light producers. They use light-emitting diodes (LEDs) to create brilliant, directed beams. These lights are made for outside jobs. Examples include building walls, bridges, and city scenes. Their tiny shape, toughness, and adaptability make them perfect for lively light shows. This differs from older choices like filament or tube lamps.
The Evolution of LED Technology
The story of LED point lights started long ago. People first saw electroluminescence in the early 1900s. This is when stuff glows faintly if electricity flows through it. Initial LEDs came in the 1950s. They gave off unseen heat rays or red light using stuff like gallium arsenide (GaAs). These were only one color. So, they weren’t good for everyday lighting. Over many years, improvements in chip materials and making methods led to stronger, better LEDs. These could make many colors, even white light.
| Milestone Year | Description |
| Electroluminescence Discovery | Early 1900s Faint light emission observed in crystal diodes. |
| First Infrared LEDs | 1950s Gallium arsenide LEDs used for basic applications. |
| Blue LED Development | 1990s Breakthrough in gallium nitride (GaN) crystals enabled blue and white LEDs. |
| Modern LED Point Lights | 2000s-Present High-brightness, durable LEDs for outdoor use. |
The creation of blue LEDs changed everything. Isamu Akasaki, Hiroshi Amano, and Shuji Nakamura led this work. They won the Nobel Prize in Physics in 2014. By mixing blue LEDs with phosphors, makers could create white light. This made LEDs fit for building and pretty lighting jobs.
The Physics of LED Point Lights
The main part of this lighting method is the pn-junction. This is a chip shape that allows light creation. Let’s look at how these lights function.
How LEDs Produce Light
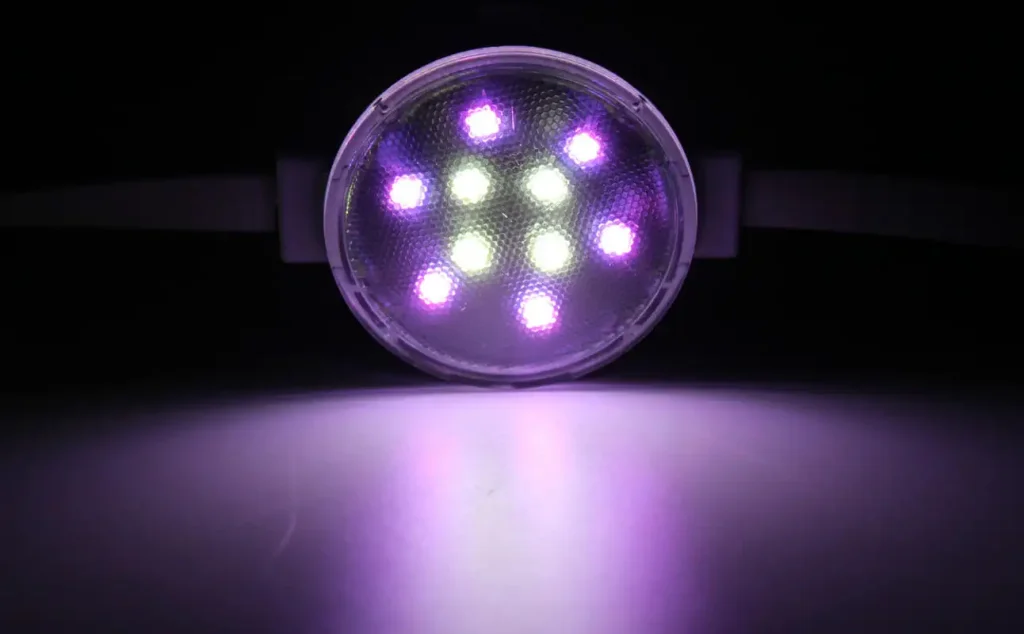
LEDs work using electroluminescence. A pn-junction has two parts. The n-type part has many electrons. The p-type part has spaces needing electrons (holes). When electricity is added, electrons from the n-type part move to the p-type part. They fill the holes. This joining releases force as photons. We see this as light.
Band Gap and Light Color: The energy difference between the two parts is the band gap. It sets the light’s wavelength. A bigger gap makes shorter waves, like blue light. A smaller gap makes longer waves, like red light.
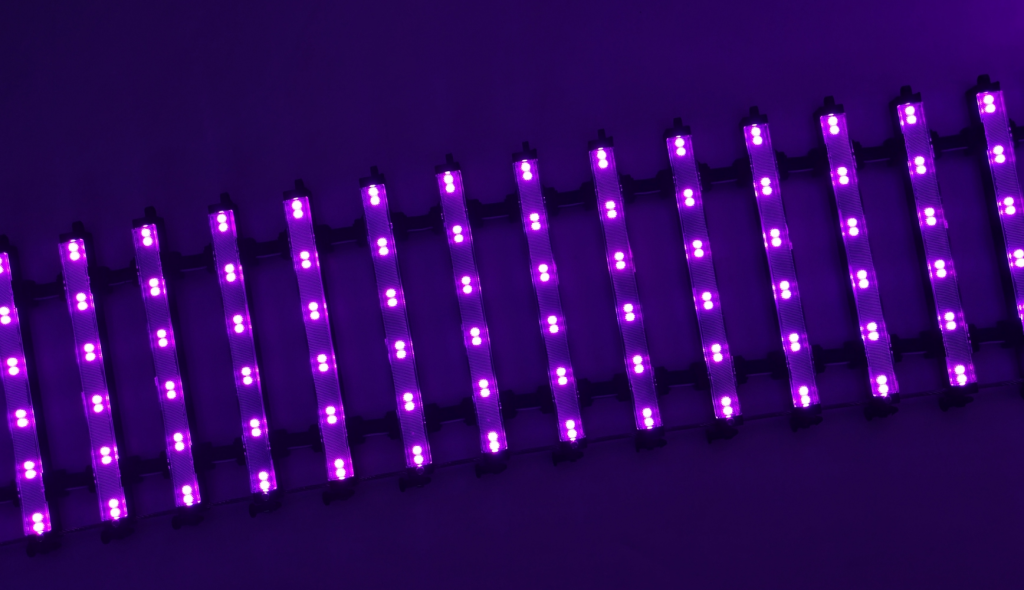
Phosphor Conversion: To get white light, blue LEDs get a coating. Phosphors take in blue light and send out other colors. These mix to make white light.
Why LED Point Lights Are Efficient
Filament bulbs make light by heating a wire. But LEDs create light with little heat loss. This makes LED point lights very economical. They turn up to 80% of electric power into light. Their effectiveness gets better because:
Low Power Use: LED point lights need much less electricity than older lights.
Long Service Life: They last up to 50,000 hours. This cuts down on swap-out and upkeep costs.
Toughness: Made for outside jobs, they resist bumps, shakes, and bad weather.
Applications of LED Point Lights
These lights are used a lot outside. They are flexible and look good. They boost the visual effect in many places, from city spots to business areas.
Architectural Lighting
LED point lights are perfect for lighting up building faces, bridges, and statues. Their small size allows exact placing. This makes detailed light shapes that show off building parts. For instance, they can trace a building’s edges or create changing color shows.
Advertising and Signage
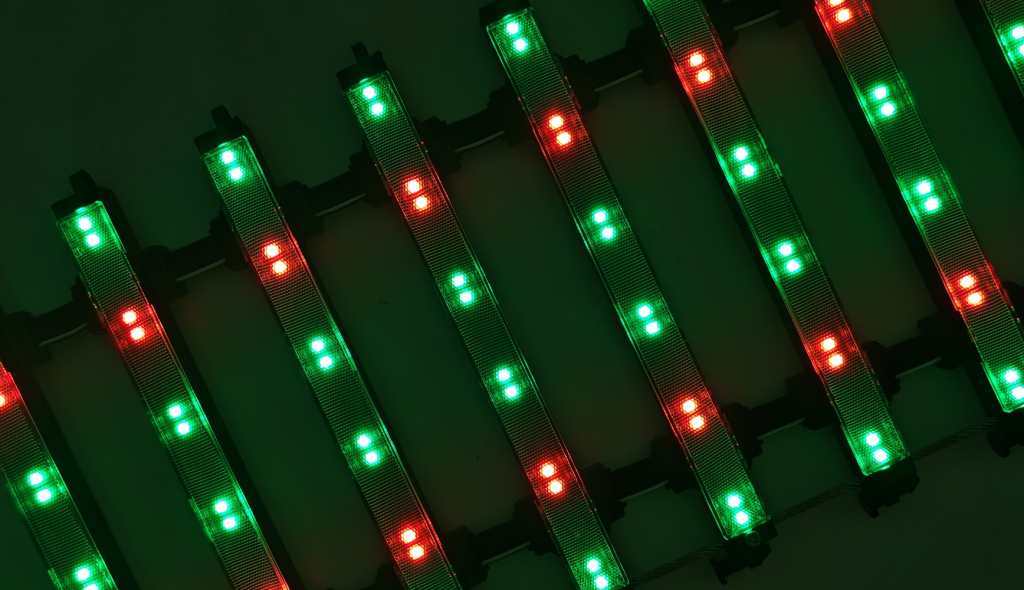
In promotion, LED point lights make attention-grabbing displays for big signs, shop fronts, and symbols. Their strong shine (up to 6000 cd/m²) ensures they are seen even in daylight. Also, they can be programmed for moving pictures and films.
Urban and Landscape Lighting
Cities use LED point lights to make shared areas nicer. Examples are parks, squares, and travel centers. They can work with clever control setups. This allows matched light effects. It improves looks and saves power.
| Application | Main Advantages |
| Architectural Lighting | Precise, customizable, durable |
| Advertising/Signage | High brightness, dynamic displays |
| Urban/Landscape Lighting | Energy-efficient, smart controls |
Technical Advantages of LED Point Lights
Current LED point lights, like those from top makers such as XinHe Lighting Optoelectronics, use new tech to boost results.
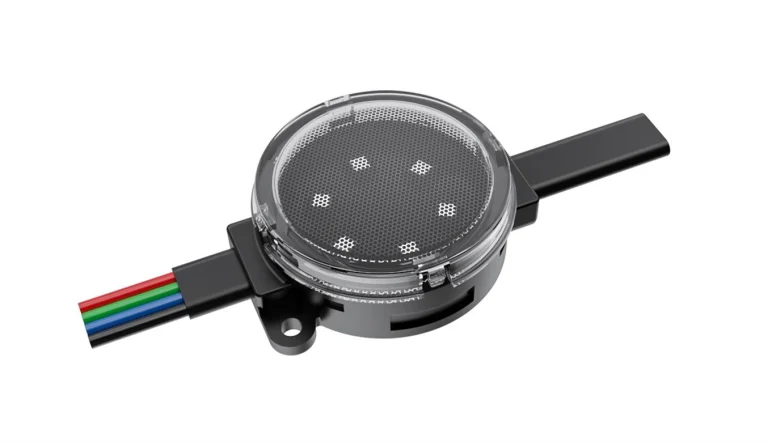
Key Features
High Shine and Steadiness: Using top chips like Epistar or Cree, they give steady, strong light with little fading.
IP67 Protection: Sealed with strong stuff like PU glue, these lights keep water out. They are good for inside and outside jobs.
Clever Control: Features like WIFI remote control, group control, and sensing parts allow lively light effects and simple running.
Tiny Plan: New covering and spread-out micro-hole heat escape keep shapes small and work well.
Comparison with Traditional Lighting
| Feature | LED Point Light | Incandescent | Fluorescent |
| Energy Efficiency | High (80% efficiency) | Low (10-15% efficiency) | Moderate (50% efficiency) |
| Lifespan | 50,000 hours | 1,000 hours | 10,000 hours |
| Durability | Shock-resistant, weatherproof | Fragile | Moderately durable |
| Light Quality | High color purity, customizable | Warm, less precise | Cool, limited spectrum |
XinHe Lighting Optoelectronics: A Trusted LED Point Light Supplier
Shenzhen XinHe Lighting Optoelectronics Co., Ltd. began in 2004. It is a top creator in LED point light and grid screen tech. Focusing on quality and new ideas, XinHe has won awards. These include National High-Tech Enterprise and Shenzhen Specialized and Innovative SME. Their “Bean” mark is famous for its unique LED point light answers. These were used in famous jobs like the 2008 Beijing Olympics.
XinHe’s LED point lights are made for outside jobs. They offer strong shine, little fading, and IP67 water blocking. Their new making steps are approved under ISO9001 and ISO14001. This ensures dependability and effectiveness. They care about buyer happiness. So, XinHe gives full services. These include plan design, project cost plans, and on-site help. This makes them a reliable partner for big lighting jobs.
Future Trends in LED Point Light Technology
The outlook for LED point lights is positive. Ongoing progress in materials, effectiveness, and clever joining will help. New ideas like better phosphors for wider light ranges and micro-LED tech promise tinier, better lights. Also, adding IoT and AI will allow smarter, more aware lighting setups. This will improve city spaces and lower energy use.
Conclusion
The science behind LED point lights joins new physics with leading tech. This gives economical, tough, and eye-catching lighting answers. From their electroluminescent roots to their current jobs in building and city lighting, they have changed how we light our world. With groups like XinHe Lighting Optoelectronics leading, the future of LED point lights promises even bigger new ideas and effect. Whether lighting a tall building or a town square, knowing the science and plus points of LED point lights helps you create brighter, longer-lasting places.
FAQs About LED Point Lights
What makes LED point lights suitable for outdoor use?
They are built to last. They have IP67 water blocking and resist bumps and shakes. Their strong shine and low power need make them ideal for lighting building faces, bridges, and city spots, even in rough weather.
How do LED point lights achieve white light?
White light happens by mixing blue LEDs with phosphors. These change blue light into other colors. This makes a wide range that looks white. This step ensures top quality, economical light for many jobs.
What are the benefits of using LED point lights over traditional lighting?
They offer better energy savings, longer lives (up to 50,000 hours), and more toughness compared to filament or tube lights. They also give changeable colors and clever control choices. This makes them flexible for lively shows.
Can LED point lights be used in smart lighting systems?
Yes, they back new control features. Examples are WIFI remote control, group control, and sensing parts. These allow matched light effects and joining with clever city setups.
How do I choose the right LED point light for my project?
Picking the right one depends on things like where it goes, how bright it must be, and the wanted effects. Talk to a trusted source like XinHe Lighting Optoelectronics. They can plan an answer made for your job’s needs.